Image
Recovering heat for re-use to cut carbon emissions
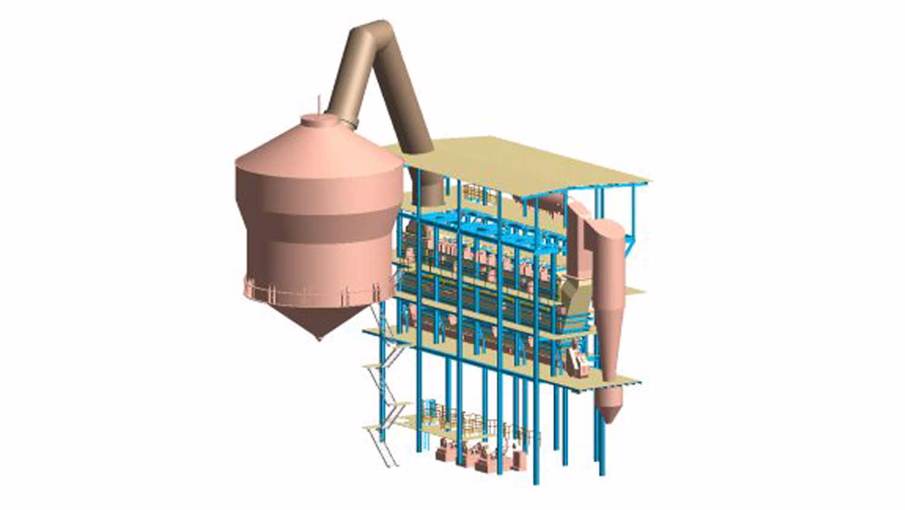
Energy efficiency is about more than the fuel itself – it’s also about making sure the power generated doesn’t go to waste. Our customers, particularly those in metallurgical industries, are using our waste heat boilers (WHB) to help them reduce their fuel consumption, carbon emissions, and environmental impact.
Tabs
WHB technology allows metallurgical plants to recover energy from hot process gases in non-ferrous pyrometallurgical furnaces or similar processes. Recovered heat improves a plant’s bottom line by producing steam for power generation, drying, and heating.
As an auxiliary process device without its own heat source, WHB technology is an important part of the metallurgical process and should not create a bottleneck. Our forced circulation boilers, with small diameter but thick wall boiler tubes, have a reliable water distribution and the tube wall structure is robust and durable. The cooling of hot process gases in WHB also allows further process dust removal in the plant, and gas cleaning such as removing and recovering sulfur at acid plants.
Reliability in the harshest conditions
- The boilers operate smoothly in very challenging environments containing corrosive hot gases and molten ash particles.
- The equipment is designed for extreme operating conditions with minimum downtime and easy and quick repair.
Self-cleaning
- Our unique patented spring hammer rapping system enables effective boiler walls and tube bank cleaning, which is critical to WHB’s efficient and reliable operation.
Customized design
- In new WHB installations, adding a variety of custom design features optimizes efficiency and utilization of plant layout. The same features can also be utilized in modernizations, modifications and upgrades for existing WHB’s, whoever originally supplied them.
WHB technology has wide applicability in the metallurgical industry – we’ve supplied over 100 WHBs around the world. The technology has been used extensively in non-ferrous metallurgical processes like copper, nickel and lead smelting, zinc and pyrite roasting, and copper and nickel converting.


